Introduction
how long should a car battery last ??????? Have you ever turned your key (or pushed the start button) only to hear a weak crank—or worse, silence? A dead car battery is one of the most frustrating car problems, especially when it happens unexpectedly.
So, how long should a car battery last? On average, a car battery lifespan is 3 to 5 years, but many factors can shorten or extend that duration. In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about car battery longevity, maintenance tips, troubleshooting solutions, and best replacement options to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Table of Contents
1. Car Battery Basics: What Every Driver Should Know

What Does a Car Battery Do?
Your car battery is the heart of your vehicle’s electrical system. It powers the starter, lights, radio, and even modern electronic components like infotainment systems and advanced driver-assistance features. Without a functioning battery, your car won’t start—no matter how new it is.
Types of Car Batteries
Not all car batteries are the same. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Lead-Acid Batteries – The most common and affordable, but require maintenance.
- AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) Batteries – More durable and used in vehicles with start-stop systems.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries – Found in hybrids and electric cars, known for longevity.
What Shortens Battery Life Unexpectedly?
- Frequent short trips that don’t allow the battery to fully charge.
- Extreme temperatures (hot weather accelerates chemical breakdown, cold weather slows performance).
- Leaving accessories (lights, phone chargers, radio) on when the engine is off.
- Alternator issues preventing proper battery charging.
2. Real-Life Factors That Kill Your Car Battery Faster
Driving Habits That Drain Your Battery
- Stop-and-go city driving puts more strain on the battery than highway driving.
- Using electronics while idling (heated seats, A/C, defroster) increases power draw.
- Not driving for long periods can lead to battery discharge and sulfation buildup.
Weather Conditions & Battery Lifespan
- Hot Climates: High temperatures accelerate water evaporation in traditional lead-acid batteries, leading to premature failure.
- Cold Climates: Batteries struggle to generate power in low temperatures, making winter starts difficult.
Electronics & Accessories: Are You Overloading Your Battery?
Modern vehicles have more electronics than ever, which means increased battery demand. GPS, infotainment, security systems, and even power tailgates can slowly drain your battery over time if your alternator isn’t keeping up.
Alternator & Charging System Failures
If your car’s alternator isn’t working properly, your battery won’t recharge correctly. Warning signs include dim headlights, electrical glitches, and a constantly illuminated battery light on your dashboard.
3. Early Warning Signs of a Dying Car Battery

- Slow Engine Crank: If your car takes longer than usual to start, your battery may be weakening.
- Dim Headlights & Interior Lights: A weak battery can’t power electrical components efficiently.
- Electrical Malfunctions: Power windows slowing down? Radio cutting in and out? These could be signs of a weak battery.
- Corrosion & Leaks: If you notice white or green buildup around the terminals, your battery may not be making a strong connection.
4. DIY Car Battery Testing & Maintenance
How to Test Your Car Battery’s Health
- Use a multimeter: A fully charged battery should read 12.6 volts or higher when the engine is off.
- Check voltage while running: 13.7 to 14.7 volts means your alternator is working properly.
- Get a load test at an auto parts store if your battery is over 3 years old.
Battery Maintenance Tips for Maximum Longevity
- Clean the terminals regularly to prevent corrosion.
- Check electrolyte levels in traditional lead-acid batteries (if applicable).
- Secure the battery properly to reduce vibrations.
- Use a battery maintainer if your car sits idle for long periods.
5. Emergency Car Battery Fixes: What to Do When Your Car Won’t Start
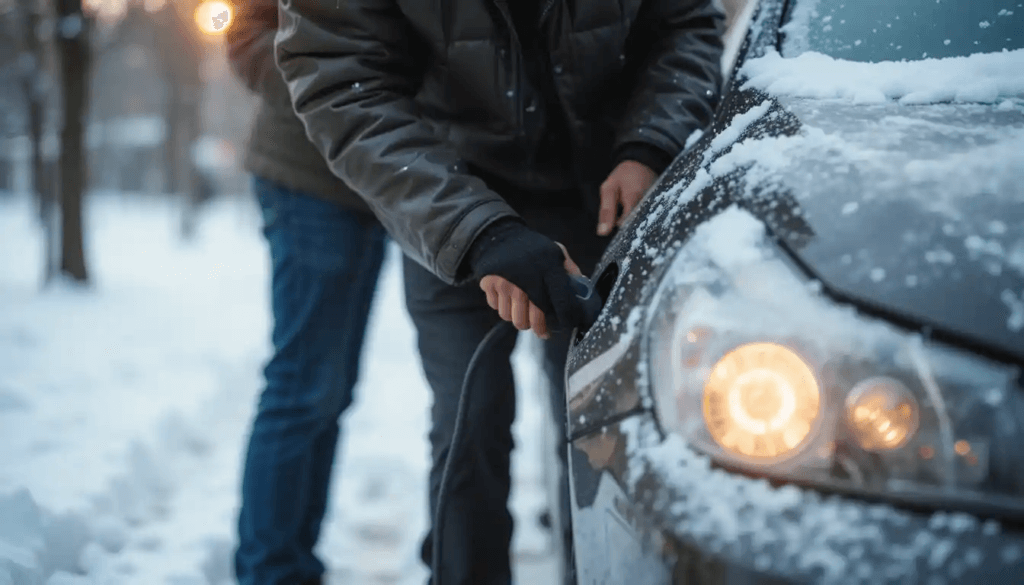

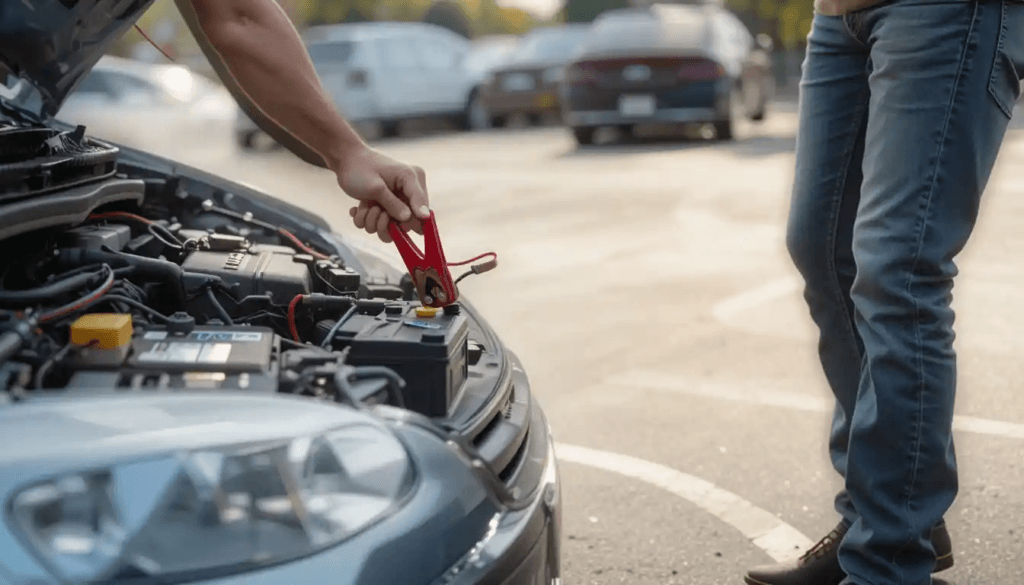
How to Jump-Start a Car Battery (The Right Way)
- Connect the red (+) clamp to the dead battery’s positive terminal.
- Attach the other red clamp to the donor car’s positive terminal.
- Connect the black (-) clamp to the donor battery’s negative terminal.
- Attach the last black clamp to an unpainted metal surface on the dead car.
- Start the donor car, let it run for a few minutes, then start the dead car.
When to Call for Roadside Assistance
- If your battery is over 5 years old and has repeatedly died.
- If jump-starting doesn’t work, your alternator or starter could be the issue.
- If there’s visible battery swelling, leaking, or a rotten egg smell.
6. Choosing the Right Battery Replacement: A Buyer’s Guide
How to Read Battery Specifications
- CCA (Cold Cranking Amps) – The higher, the better for cold weather.
- RC (Reserve Capacity) – Determines how long the battery can run essential components.
- Amp-Hours (AH) – A higher rating means longer-lasting performance.
Best Car Battery Brands for Long Life
- Optima (AGM technology, long lifespan)
- DieHard (Strong warranties, reliable performance)
- ACDelco (OEM choice for many manufacturers)
Best Warranty Options for Replacements
Look for warranties offering 3+ years of free replacement coverage for added value.
7. Prolonging Battery Life: Expert Tips & Little-Known Hacks
- Drive at least 20-30 minutes weekly to keep the battery charged.
- Turn off headlights, AC, and radio before shutting off the engine.
- Use a battery tender for long-term parked cars.
- Keep terminals greased to prevent corrosion.
8. Car Battery Myths That Mechanics Hate
- Myth: “Car batteries last 10 years.” (False) Most last 3-5 years.
- Myth: “Idling charges your battery.” (False) The alternator needs higher RPMs to charge effectively.
- Myth: “Premium batteries last forever.” (False) Even the best brands degrade over time.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Your car battery is one of the most important yet overlooked parts of vehicle maintenance. By understanding its lifespan, warning signs, and how to extend its life, you can avoid unexpected breakdowns and costly replacements.

